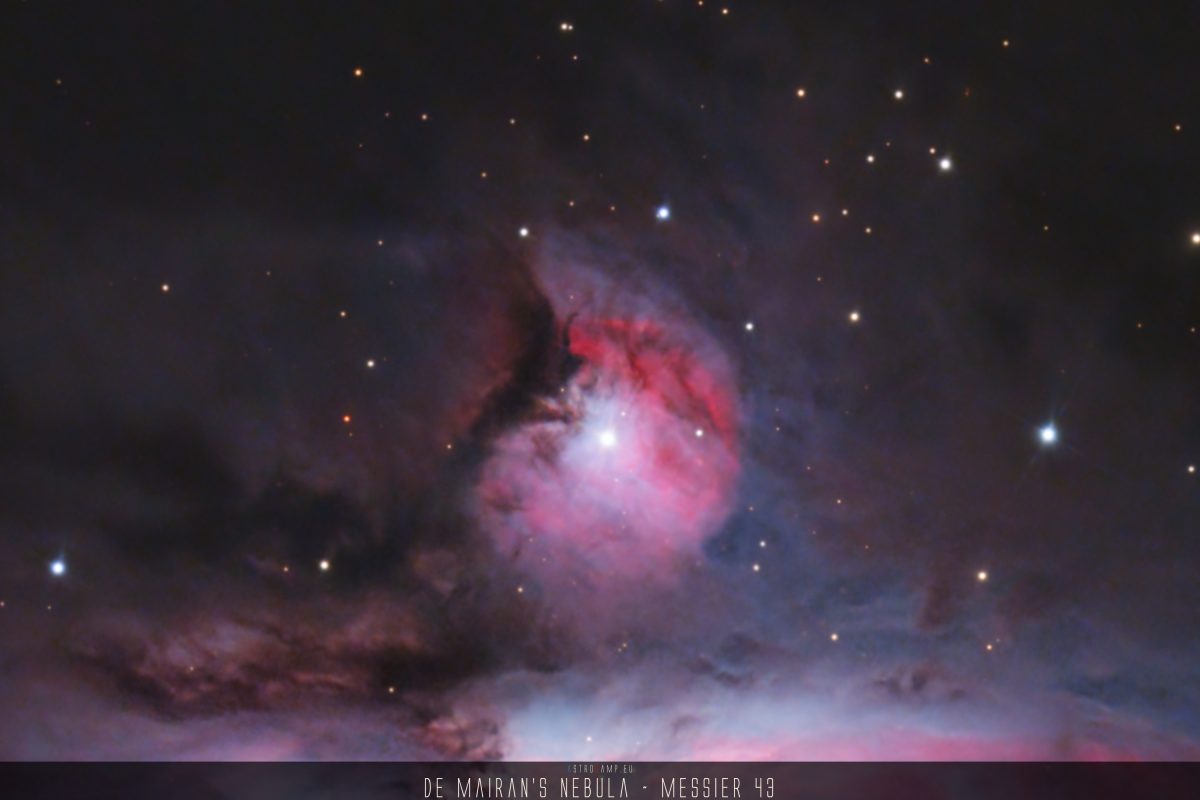
Messier 43, commonly known as De Mairan’s Nebula, is an emission nebula located within the Orion constellation. It is a part of the larger Orion Molecular Cloud Complex. The nebula is illuminated by nearby stars, creating a visually striking and intricate celestial formation. Its presence contributes to the overall beauty and complexity of the stellar environment in the Orion constellation.
Location and neighborhood.
Messier 43 is located in the constellation Orion, which is one of the most prominent and recognizable constellations in the night sky. To be more specific, it is situated just below the three prominent stars forming Orion’s Belt. If you imagine Orion as a hunter, Messier 43 would be found near his sword, which hangs down from the “belt” of three stars.
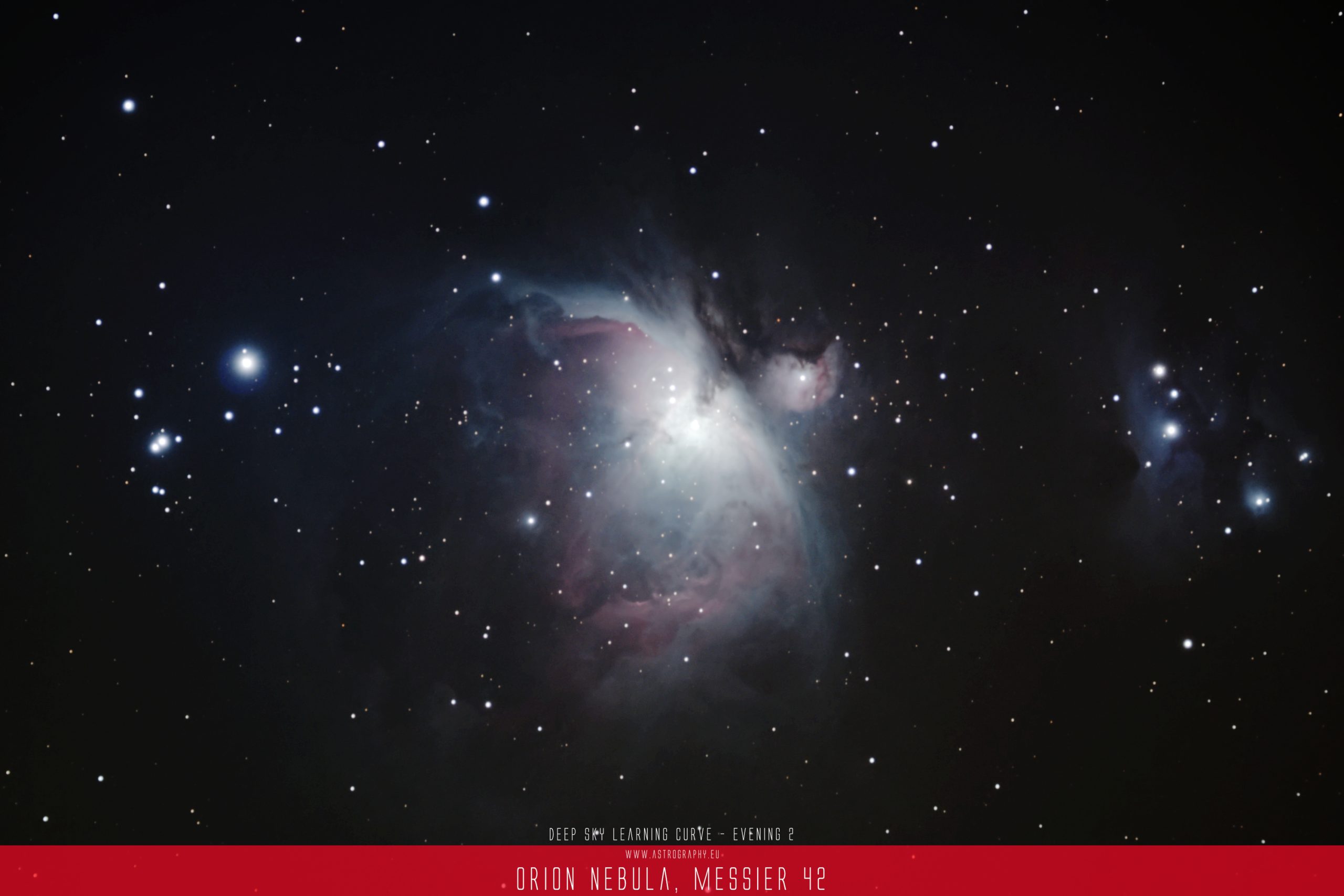
The Orion Molecular Cloud Complex is a significant site for ongoing star formation. The gas and dust within these clouds serve as the raw material from which new stars and planetary systems emerge. The Trapezium Cluster, a young and hot cluster of stars, is particularly noteworthy within the Orion Nebula and contributes to the ionization and illumination of the surrounding gas.
In summary, Messier 43 is part of a dynamic cosmic neighborhood characterized by active star formation, illuminated nebulae, and the presence of young stellar clusters, all within the captivating Orion Molecular Cloud Complex.
Unique facts
- Messier 43 is located in the Orion constellation, specifically in the region often referred to as Orion’s Sword, hanging below the three distinctive stars forming Orion’s Belt.
- Messier 43 is also known as De Mairan’s Nebula, named after the French astronomer Jean-Jacques Dortous de Mairan, who first described it in 1731.
- Messier 43 is part of the larger Orion Molecular Cloud Complex, a vast region of gas and dust where new stars are actively forming. This complex includes other notable features such as the Orion Nebula (Messier 42) and the Horsehead Nebula.
- The Trapezium Cluster, a young and hot cluster of stars located within the Orion Nebula, contributes to the ionization and illumination of Messier 43. The energy and radiation from these young stars play a role in shaping the appearance of the nebula.
Brightness and size
The distance to Messier 43 is part of the Orion Molecular Cloud Complex, which is located at a distance of approximately 1,344 light-years from Earth. This distance is an average for the entire complex, and Messier 43 would be within this general vicinity.