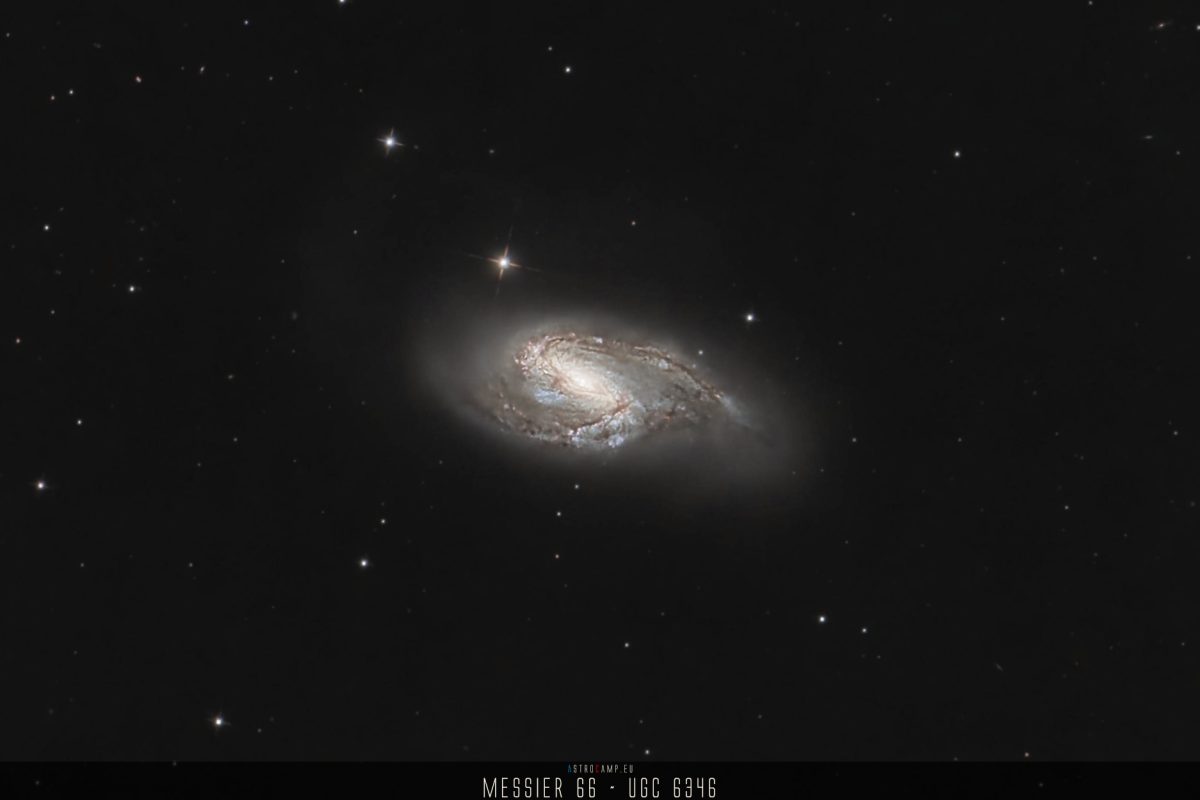
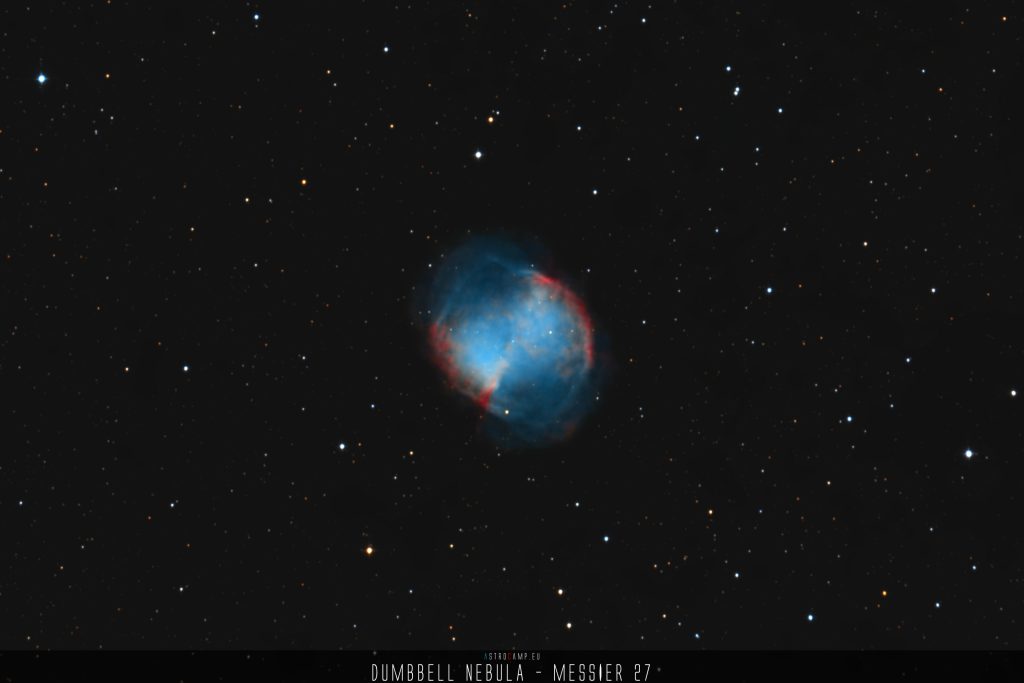
Messier 66, also known as M66, is a spiral galaxy situated approximately 36 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation Leo. It is one of the members of the Leo Triplet, a small group of galaxies that includes M65 and NGC 3628. M66 exhibits prominent spiral arms and is undergoing significant star formation activity, evidenced by its numerous H II regions and young, bright blue stars. The galaxy was discovered by Charles Messier in 1780, and its appearance is distorted due to gravitational interactions with its neighboring galaxies.
List of Catalog Numbers
- Messier 66
- UGC 6346
- NGC 3627
Position and Cosmic Neighborhood
Messier 66 lies within the constellation Leo and is part of the Leo Triplet, a small group of galaxies situated in the eastern part of Leo. This triplet is relatively close to the ecliptic plane, making it easily observable from Earth’s northern hemisphere during spring.
Four Special Facts
- Messier 66 is a member of the Leo Triplet, a small group of galaxies.
- It exhibits prominent spiral arms and active star-forming regions.
- The galaxy’s appearance is distorted due to gravitational interactions with neighboring galaxies.
- Messier 66 was discovered by Charles Messier in 1780.
Brightness, Distance, and Size
Messier 66 is a spiral galaxy with a brightness of magnitude 8.9. It is located approximately 36 million light-years away from Earth and spans approximately 95,000 light-years in diameter. The angular size of Messier 66 is approximately 8.9 arcminutes.