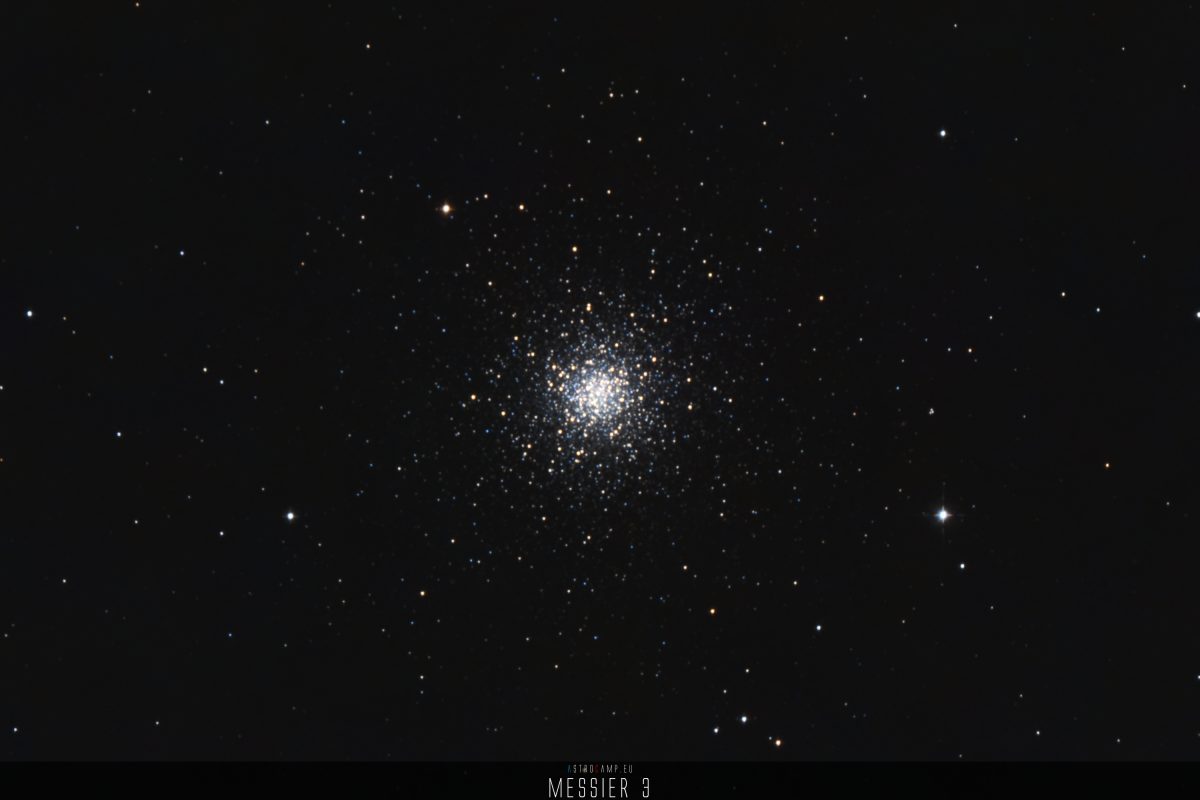
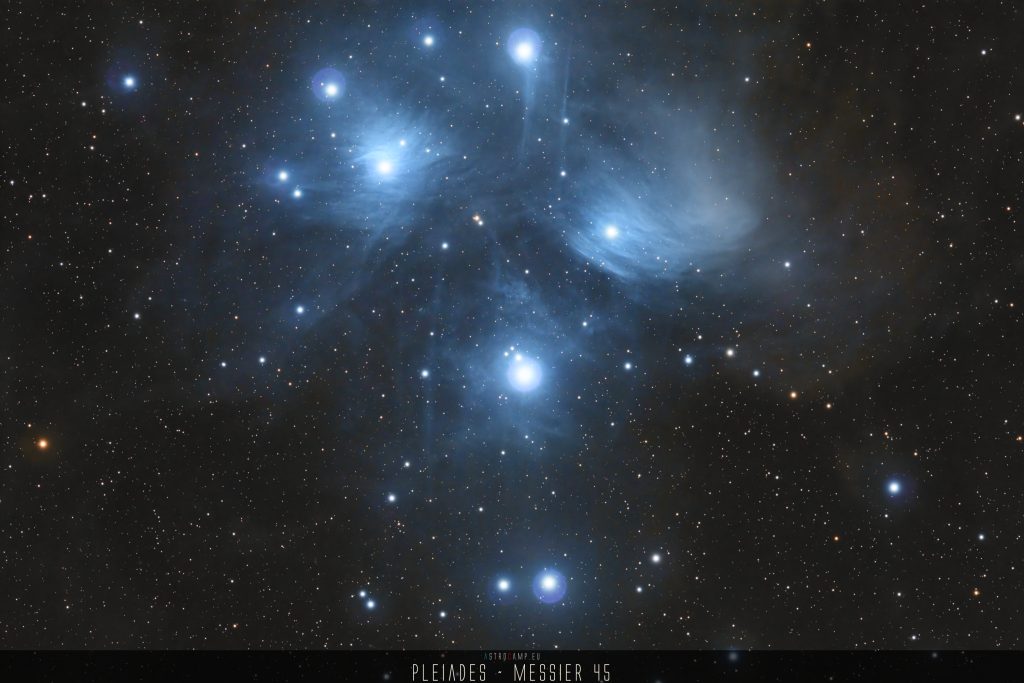
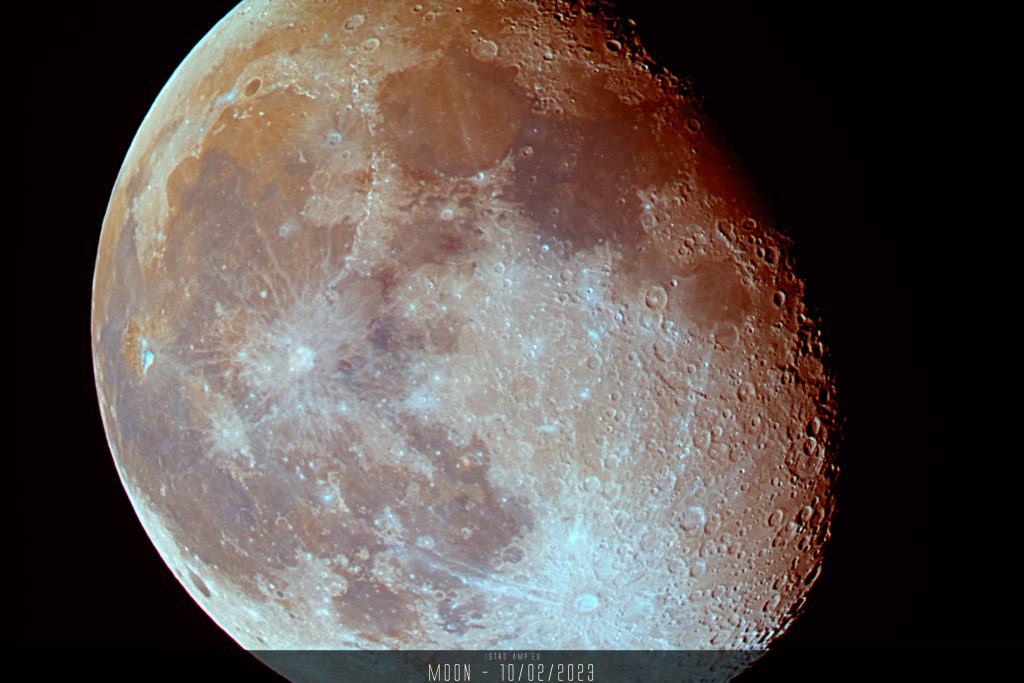
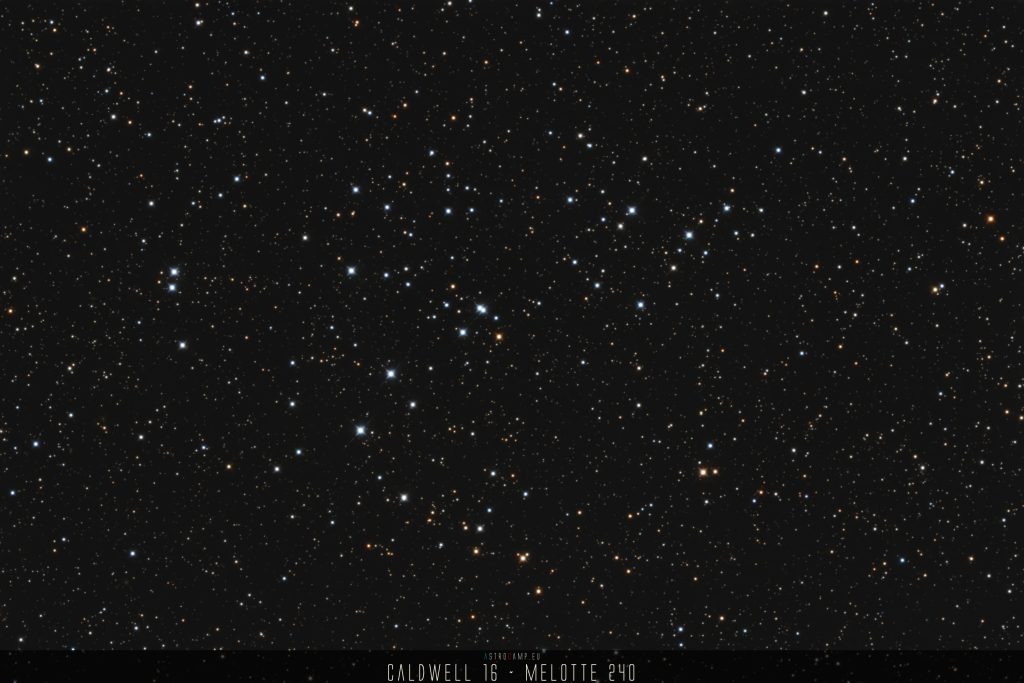
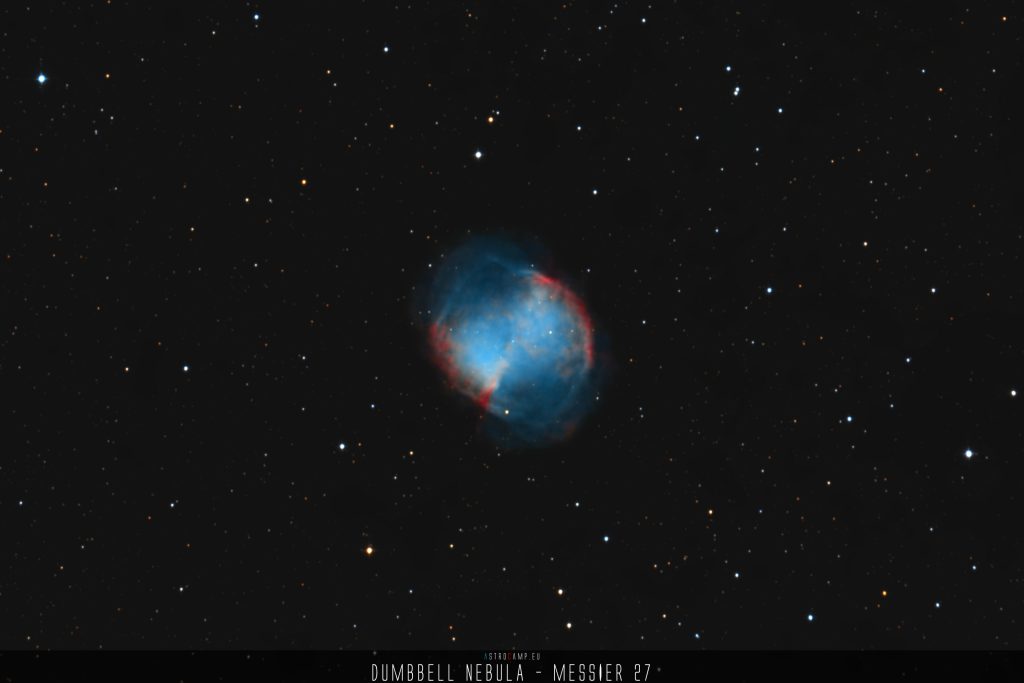
Messier 3 is an impressive globular cluster located in the constellation Canes Venatici, approximately 33,900 light-years away from Earth. It contains several hundred thousand stars, including many ancient stars formed billions of years ago. The high stellar density and compact structure make Messier 3 a fascinating celestial object for astronomers and amateur stargazers alike.
Location and neighborhood.
Messier 3 is located in the constellation Canes Venatici, often considered a companion to the constellation Ursa Major. More specifically, Messier 3 is situated approximately 33,900 light-years away from Earth and about 8 degrees northwest of Arcturus, the principal star in the constellation Boötes. It is one of the brightest and well-known globular clusters in the night sky, visible with a telescope or even with good binoculars.
Unique facts
- Messier 3 is one of the oldest globular clusters, estimated to be around 11.4 billion years old. It hosts an impressive number of stars, with an estimated total star count ranging from several hundred thousand to a million.
- Messier 3 is one of the brightest globular clusters visible from Earth. Its apparent brightness makes it a popular target.
- Messier 3 is notable for being the site where the first known variable star, XZ Cancri, was discovered.
Brightness and size
Messier 3 is one of the brightest globular clusters visible from Earth, with an apparent magnitude of around 6.2. This makes it visible to the naked eye under dark sky conditions.
The physical size of Messier 3 is impressive, spanning about 180 light-years in diameter. This measurement includes the densely packed concentration of stars within the cluster.
The apparent size of Messier 3 in the night sky is relatively small, occupying an angular diameter of approximately 18 arc minutes. While this makes it challenging to observe its individual stars without the aid of a telescope, its concentrated brightness contributes to its visibility even in modest-sized instruments.