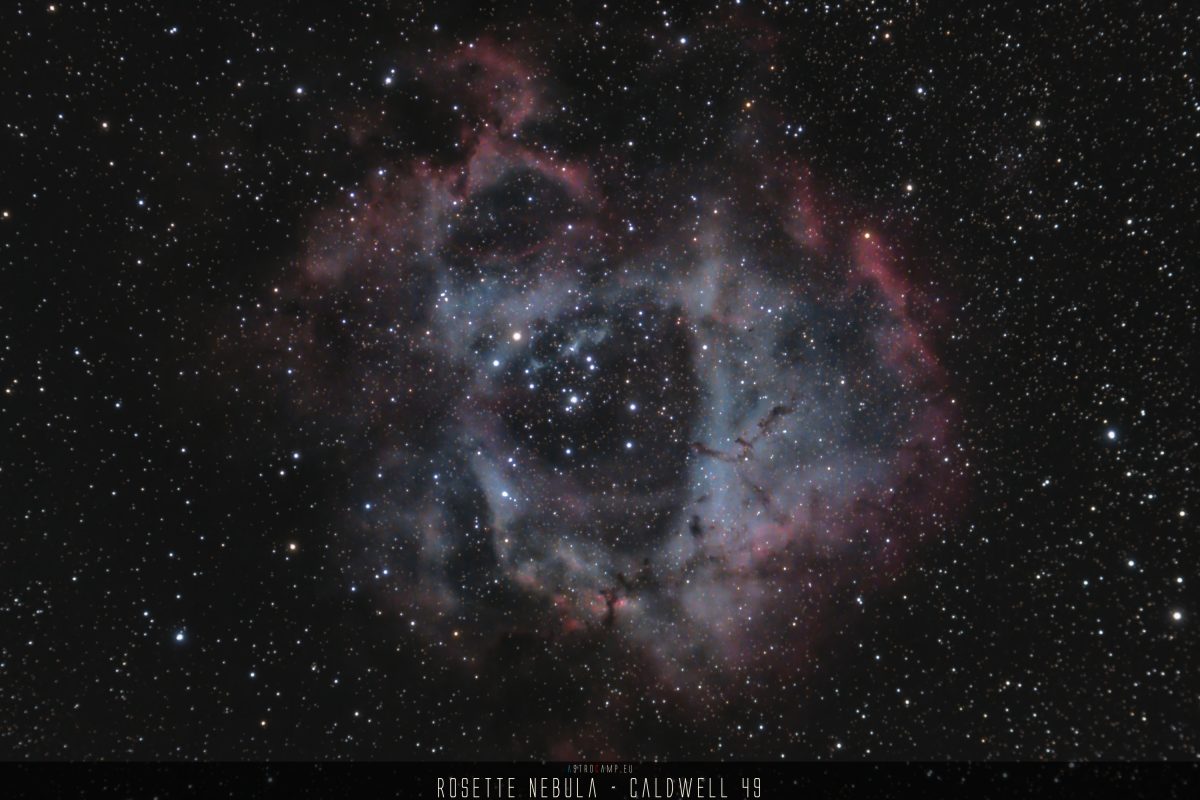
The Rosette Nebula, located in the constellation Monoceros, is a vast region of glowing hydrogen gas and dust. This stellar nursery is home to the open star cluster NGC 2244, whose massive, hot stars emit intense ultraviolet radiation. The radiation causes the surrounding hydrogen gas to fluoresce, creating the nebula’s distinctive rose-like appearance. The Rosette Nebula is a site of ongoing star formation, offering a spectacular celestial display and providing astronomers with valuable insights into the processes of stellar birth and evolution.
Location of Caldwell 49
The Rosette Nebula consists of several nebular regions that collectively contribute to its complex and captivating appearance. Here are some of the key nebulae that make up the Rosette Nebula:
- NGC 2244: NGC 2244 is an open star cluster within the Rosette Nebula. The radiation from the young stars in this cluster contributes to illuminating the surrounding nebula.
- Rosette Nebula NGC 2237: This is the central region of the Rosette Nebula. It is an emission nebula illuminated by the ionizing radiation from the stars in the open cluster NGC 2244.
- Rosette Nebula NGC 2238, NGC 2239, NGC 2246, and NGC 2247: These are part of the emission nebula, illuminated by the emission of hydrogen gas and other ionized elements.
Together, these nebular regions create an impressive astronomical object that yields spectacular images when observed in various wavelength ranges, including visible light and infrared.
The Rosette Nebula is located in the constellation Monoceros and can be found south of Sirius, the Dog Star, and east of Orion’s Belt. Due to its proximity to the celestial equator, the Rosette Nebula is visible from many regions on Earth.
Unique facts
- The distinctive rosette shape of the nebula is the result of the interaction between the high-energy radiation from the young stars in NGC 2244 and the surrounding hydrogen gas. This process leads to the ionization of the gas and the emission of light, creating the characteristic pinkish structure.
Brightness and size
The Rosette Nebula exhibits moderate brightness, spans several hundred light-years in physical size, and presents a conspicuous apparent size in the sky, subject to variation based on location and telescope used.