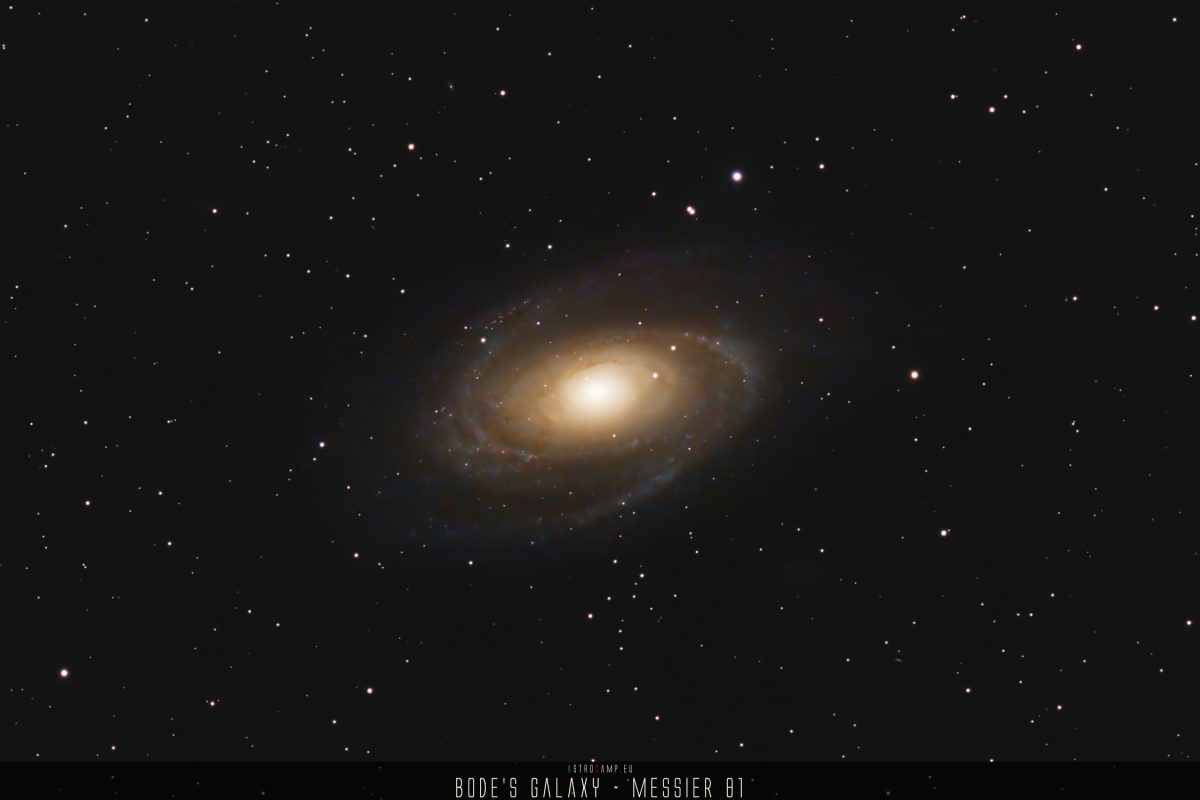
Messier 81, also known as Bode’s Galaxy, is a beautiful spiral galaxy located in the constellation Ursa Major, about 12 million light-years away from Earth.
One of the most striking features of Messier 81 is its bright central bulge, which is surrounded by intricate spiral arms that are filled with dust, gas, and young blue stars. These spiral arms extend outwards from the central bulge and are dotted with clusters of hot, bright stars and glowing nebulae.
In addition to its stunning appearance, Messier 81 is also a fascinating object of study for astronomers. It is one of the brightest galaxies in the sky and provides important insights into the formation and evolution of galaxies. Overall, Messier 81 is a breathtaking sight in the night sky and a reminder of the immense beauty and complexity of the universe.
Position and region

Messier 81 is located in the constellation Ursa Major, which is also known as the Great Bear, and is about 12 million light-years away from Earth. It is part of the M81 Group, a group of galaxies that includes several other nearby galaxies such as Messier 82, NGC 2403, and NGC 4236.
The M81 Group is itself part of a larger structure known as the Virgo Supercluster, which is a massive cluster of galaxies that contains hundreds of individual galaxies. The Virgo Supercluster spans a region of space that is about 110 million light-years in diameter and includes several other galaxy clusters, including the Fornax Cluster, the Coma Cluster, and the Hydra Cluster.
Unique facts
- Messier 81 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Ursa Major, about 12 million light-years away from Earth.
- The galaxy has a diameter of about 90,000 light-years and contains about 250 billion stars.
- Messier 81 is one of the brightest galaxies in the sky in terms of its infrared emission, which is a signature of active star formation.
- The galaxy’s central bulge contains an active galactic nucleus (AGN) that is powered by a supermassive black hole that is about 70 million times the mass of the Sun.
Brightness and size
Messier 81 is a relatively bright galaxy in the night sky, with an apparent visual magnitude of about 6.9. In terms of size, the galaxy has a diameter of about 90,000 light-years, making it roughly the same size as our Milky Way galaxy. However, Messier 81 is somewhat smaller than the Andromeda Galaxy, which is the largest member of the Local Group of galaxies that includes our Milky Way.
In terms of apparent size, Messier 81 appears quite large in the night sky due to its proximity to Earth. Its apparent size is about 21 arcminutes by 10 arcminutes, which is roughly 1/3 the size of the full moon. This makes it a popular target for amateur astronomers and astrophotographers. However, even with a small telescope, it is difficult to see much detail in the galaxy beyond its bright central bulge and spiral arms.
Names and numbers
- Bode’s Galaxy – A name given to it by Johann Bode, who discovered it in 1774.
- M81, Messier 81 – The number given to it by Charles Messier in his catalog list.
- NGC 3031 – Its catalog number in the New General Catalogue.
- UGC 5318
- PGC 28630